What is the Most Effective Treatment for ADHD?
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a condition that begins before the age of 12, but symptoms may persist throughout adulthood. There are three subtypes of ADHD.
1. Predominantly Inattentive Presentation:
-
Often fails to give close attention to details or makes careless mistakes in school, work, or other activities.
-
Often has difficulty sustaining attention in tasks and is easily distracted.
-
Often does not follow through on instructions and fails to finish tasks.
-
Often has difficulty organizing.
-
Often avoids, dislikes, or is reluctant to engage in tasks that require a lot of effort.
-
Is often forgetful.
2. Predominantly Hyperactive-Impulsive Presentation:
-
Often fidgets with hands or feet or squirms in seat.
-
Often interrupts or intrudes on others.
-
Often has difficulty waiting their turn.
-
Often talking excessively and blurts out answers before questions have been completed.
-
Often "on the go," acting as if "driven by a motor."
-
Often leaves seat in situations where remaining seated is expected.
3. Combined Presentation : symptoms include both inattention and hyperactivity-impulsivity.
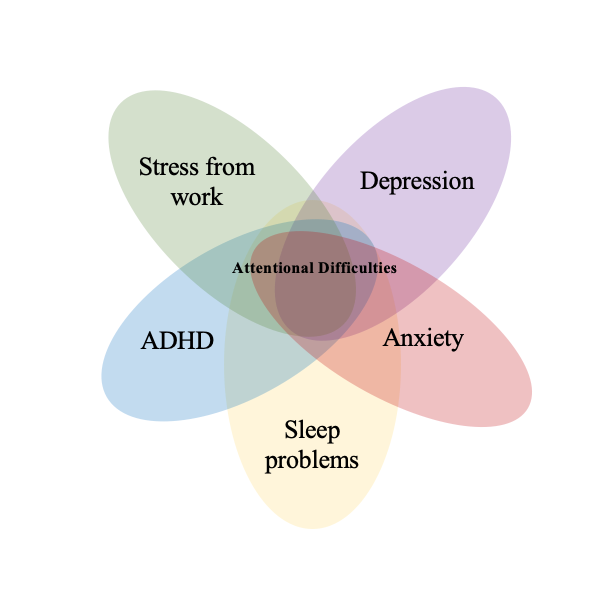
These symptoms must cause impairment in functioning in school, work, or socially in relationships. Importantly, these symptoms cannot be better explained by another mental health condition. If you have been diagnosed with ADHD as a child, and you are struggling with inattentiveness or hyperactivity as an adult, you may assume your symptoms continue to be a result of ADHD. However, ADHD is often comorbid with other conditions such as depression and anxiety. Depression and anxiety may also affect your attentional abilities!
For example, you’re at work and your supervisor is telling you about a deadline for a project next week. You have a hard time paying attention to her because you haven’t started (anxiety), are unmotivated and lack the energy to do anything (depression), and you’re not sleeping well because of it all.
So, what is causing these attentional difficulties? Is it ADHD or depression or anxiety or lack of sleep or stress? It can be all the above!
If you are newly diagnosed, one of the first steps you may consider is medications as it may be a “quick fix.” Medications can helpful, however the most effective ADHD treatment includes a combination of medications, therapy and psychoeducation.
What would therapy for ADHD look like?
1. For those with attentional difficulties, having structure and routine is extremely important. This external structure can be implemented by utilizing a daily planner or calendar to keep organized and schedule things ahead. You will also learn strategies to set clear and realistic goals, prioritize tasks, and break down overwhelming tasks into manageable steps to maximize success.
2. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) involves reframing negative thinking patterns and behaviors. CBT is not only effective in treating ADHD, but also depression and anxiety. CBT helps “slow down” your thinking so you can reflect on what is preventing you from making those deadlines, changing unhelpful thoughts to manage emotions, and learn problem solving skills.
3. Mindfulness-Based Exercises involve actively paying attention to your thoughts, feelings, and physical sensations in your body. With regular practice, this can help improve your ability to sustain attention. Mindfulness can also help reduce anxiety and stress as it promotes relaxation.
Where can I get help?
At Memory Gains, with the guidance of a psychologist we can sort out what is causing your attentional difficulties and work on these issues simultaneously. The good news is when you see gains in one area (reduction in depression, improvement of ADHD symptoms) you may notice improvement in other areas as well! We offer free 15-minute consultations and can tailor a specific treatment plan that meets your needs. Let’s get your life on track!
Sahra Kim Psy.D.
Email: kim@memory-gains.com
Phone: 617-249-4784
*serving Massachusetts residents only
Explore More Articles







